That includes quotas and price controls. The second aspect of public goods is what economists call nonrivalrous consumption.

Terms And Concepts For Regional Integration Integrity Terms Concept
The concept of non-economic goods is relative to place and time.
. Cross-price elasticity of demand change in quantity demanded of good A change in price of good B If good A is a substitute for good B like coffee and tea then a higher price for B will mean a. A merit good has two characteristics. Conversely the ownership of services is non-transferable.
Gross national product GNP is the value of final goods and services produced by residents of the United States even if the production takes place outside the United States. 7 differences between goods and services 1 Ownership is not transferred. Resources that arent scarce eg.
Examples of non-economic goods are air water sunshine etc. Classical vs Keynesian. The central plan sets the priorities for the production of all goods and services.
Therefore in a free market there will be under consumption of merit goods. If the free-rider problem cannot be solved valuable goods and services ones that people want and otherwise would be willing to pay for will remain unproduced. When buying a service the service ownership is not transferred to the end customer.
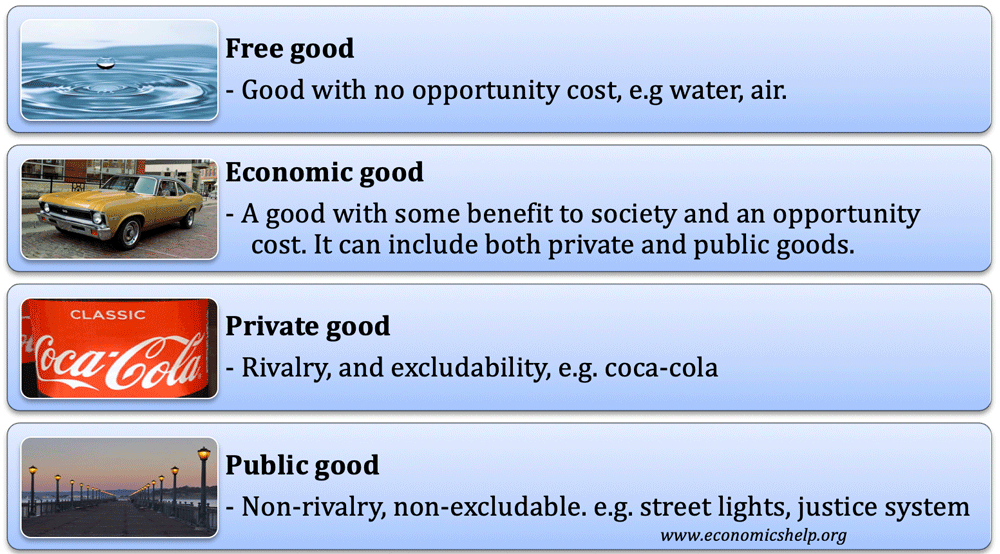
Goods can be classified as durable and non-durable based on their durability. Non-economic goods are called free goods because they are free gifts of nature. Examples of goods are furniture clothes and automobiles.
The goods categorized under public goods benefit even those who have not paid for it. In this sense all material goods are economic goods. When the buyer purchases the goods by paying the consideration the ownership of goods moves from the seller to the buyer.
Evaluate the implications of a particular course of action using the concept of opportunity cost. Distinguish between economic and free goods. Private goods public goods common resources and club goods.
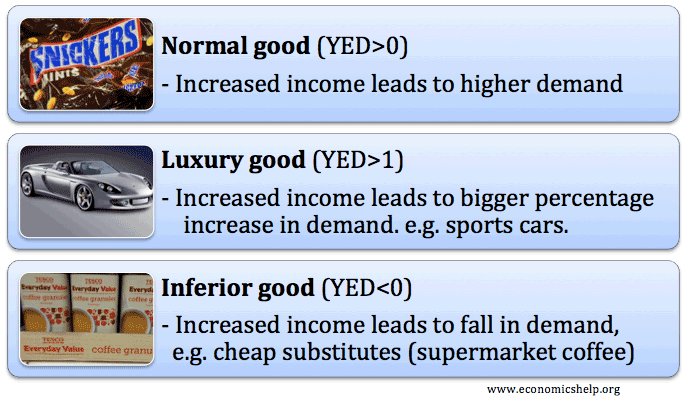
The evaluation of services is difficult because every service provider has a different approach of carrying out services so it is hard to judge whose services are better than the. Briefly explain whether the difference is important for the United States. Those goods whose demand rises with an increase in the consumers income is called normal goods.
There are four different types of goods in economics which can be classified based on excludability and rivalrousness. Explore the definition and examples of complementary goods in economics. Therefore companies which produce such products are required to pay special attention to the marketing advertising.
FMCG goods are those goods which are consumed fast and there is quite high ate of repurchase of such goods. The two schools of economic thought are related to each. Briefly explain one effect of laissez-faire economic policies in the Gilded Age.
Note that the rate at which demand increases is lower than the rate at which income increases. Classical economics and Keynesian economics are both schools of thought that are different in approaches to defining economics. Supply and demand also decide investment decisions production and distribution.
Capital goods are different from financial capital which refers to the funds companies use to grow their businesses. In a theoretical market economy supply and demand through free competition should determine prices. In economics complementary products are goods or services that consumers use together such as ski boots and ski poles.
Non-economic goods are free gifts of nature which are available free of cost. Usually these goods also have a positive externality. The difference between normal and inferior goods can be clearly drawn on the following grounds.
Resources that are scarce and that we need to pay for. The meaning of goods can be expressed in terms of economics as any item that provides utility and fulfills the needs of the consumer. Classical economics was founded by famous economist Adam Smith and Keynesian economics was founded by economist John Maynard Keynes.
The rate eventually slows down with further increments in income. Soap dresses table etc. The purpose of both goods and services is to provide utility and satisfaction to the consumer.
Briefly describe laissez-faire economic policies in the Gilded Age. Explain the main differences between pure public goods and impure public goods very briefly and discuss why the government needs to produce these types of the goods arrow_forward Explain why the private provision of public goods leads to an inefficient level of public goods. Private Goods are products that are excludable and rival.
If you buy a car then the car is yours. Public goods describe products that are non-excludable and non-rival. Normal goods are goods whose demand increases with an increase in consumers income.
They do not have any price and are unlimited in supply. Natural resources not modified by human hands are not considered capital goods. While on the other hand gross national product which is to say GNP is the total value of all the finished goods and the services produced by the citizens of the country.
Those goods whose demand decreases with an increase in consumers income beyond a certain level is called inferior goods. Material goods are those that can be touched or seen have a definite shape and size and can be shifted from one place to another. Definition of Merit Good.
Examples of Merit Goods. But if you buy a ticket for an airline. Specifically the cross-price elasticity of demand is the percentage change in the quantity of good A that is demanded as a result of a percentage change in the price of good B.
People do not realise the true personal benefit. Material and non-material goods. Briefly describe one key historical similarity or difference between laissez-faire economic policies in the Gilded Age and economic policies in the Jacksonian Era.
The consumption of such goods cannot be dismissed or unaccepted by the public since it is available collectively to all the people. We have seen that GDP is the value of final goods and services produced within the United States. These goods are usually free of cost and can be used by anyone without any restriction.
Briefly we can say that the Gross Domestic Product or the GDP is the value of finished goods and services of the nation at the domestic level and in the specific period. For example people underestimate the benefit of education or getting a vaccination.

Economic Goods Definition And Examples Economics Help

Economic Goods Definition And Examples Economics Help
Different Types Of Goods Inferior Normal Luxury Economics Help
0 Comments